Introduction: In our increasingly interconnected world, critical infrastructure plays a vital role in supporting essential services and maintaining societal functions. However, the reliance on technology and connectivity also exposes critical infrastructure to cyber threats and attacks. In this article, we will explore the crucial role of cybersecurity in protecting critical infrastructure and preventing cyber attacks.
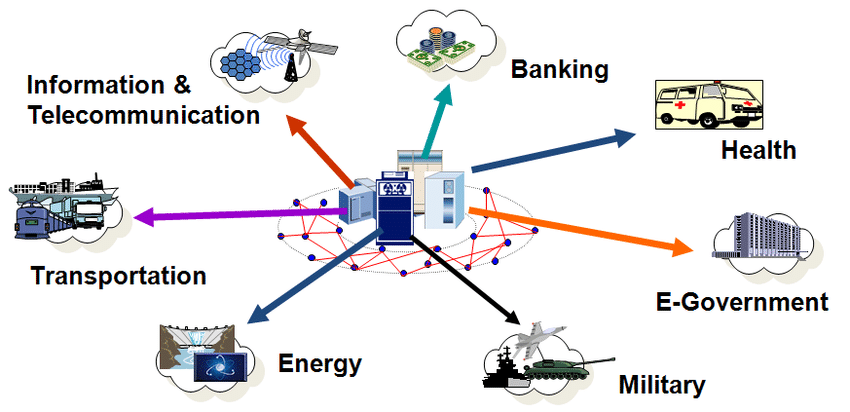
I. Understanding Critical Infrastructure:
- Definition and Examples:
- Defining Critical Infrastructure: Critical infrastructure refers to the systems and assets that are essential for the functioning of society, including energy, transportation, communication, water, and financial systems.
- Examples of Critical Infrastructure: Power grids, transportation networks, telecommunication networks, healthcare systems, and industrial control systems.
- Vulnerabilities and Consequences:
- Cyber Threats: Critical infrastructure is vulnerable to various cyber threats, such as hacking, malware, ransomware, and insider attacks.
- Potential Consequences: Cyber attacks on critical infrastructure can lead to disruptions in essential services, financial losses, public safety risks, and compromised national security.
II. The Importance of Cybersecurity for Critical Infrastructure:
- Protecting Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability:
- Confidentiality: Cybersecurity measures safeguard sensitive data and protect it from unauthorized access or disclosure.
- Integrity: Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of critical infrastructure systems and preventing unauthorized modifications or tampering.
- Availability: Maintaining the continuous operation of critical infrastructure systems, preventing service disruptions due to cyber attacks.
- Threat Detection and Prevention:
- Risk Assessment: Conducting comprehensive risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities, assess potential threats, and develop proactive cybersecurity strategies.
- Intrusion Detection Systems: Implementing advanced monitoring systems that can detect and respond to potential cyber threats in real-time.
III. Cybersecurity Measures for Critical Infrastructure Protection:
- Network Security:
- Firewalls and Intrusion Prevention Systems: Deploying robust network security measures to monitor and filter network traffic, preventing unauthorized access and malicious activities.
- Secure Network Architecture: Implementing secure network designs, including segmentation and isolation of critical infrastructure systems from external networks.
- Access Control and Authentication:
- Strong Authentication: Implementing multi-factor authentication and robust access control mechanisms to verify and authorize user access to critical infrastructure systems.
- Privileged Account Management: Enforcing strict controls and monitoring for privileged accounts to prevent unauthorized access and misuse.
- Incident Response and Recovery:
- Incident Response Plans: Developing comprehensive incident response plans to guide organizations in detecting, containing, and recovering from cyber attacks on critical infrastructure.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: Implementing robust backup and recovery mechanisms to ensure the availability and integrity of critical data and systems in the event of a cyber attack.
IV. Collaborative Efforts and Regulations:
- Public-Private Partnerships:
- Information Sharing: Encouraging collaboration and information sharing between government entities, critical infrastructure operators, and cybersecurity organizations to improve threat intelligence and response capabilities.
- Industry Standards and Best Practices: Promoting the adoption of cybersecurity frameworks and best practices across critical infrastructure sectors.
- Government Regulations and Compliance:
- Regulatory Frameworks: Enforcing cybersecurity regulations and standards to ensure the protection of critical infrastructure and incentivize organizations to prioritize cybersecurity.
- Compliance and Audits: Conducting regular compliance assessments and audits to ensure adherence to cybersecurity requirements and identify potential vulnerabilities.
Conclusion: The protection of critical infrastructure is of paramount importance in the face of evolving cyber threats. By implementing robust cybersecurity measures, including network security, access control, incident response, and collaborative efforts, we can mitigate risks, safeguard essential services, and protect national security. As technology continues to advance, a collective and proactive approach to cybersecurity is essential to stay one step ahead of
cybercriminals and ensure the resilience of our critical infrastructure systems.

